Understanding Market Cycles: When to Buy, Hold, and Sell
Investing in real estate requires a keen understanding of market cycles. These cycles, which consist of various phases, can significantly impact your investment decisions and outcomes. By knowing when to buy, hold, or sell, you can maximize your returns and minimize risks. This article will explore the different stages of the real estate market cycle and provide data to help you make informed decisions.
The Four Phases of the Real Estate Market Cycle
The real estate market typically goes through four distinct phases: Recovery, Expansion, Hyper Supply, and Recession. Each phase offers unique opportunities and challenges for investors.
1. Recovery
The Recovery phase follows a downturn in the market. During this time, property values are low, and vacancy rates are high. The market is often characterized by low demand, minimal new construction, and declining prices. However, this phase also presents a prime opportunity for investors to purchase undervalued properties.
Key Indicators:
- Low property prices
- High vacancy rates
- Low levels of new construction
Investment Strategy:
- Buy: Look for distressed properties or undervalued assets.
2. Expansion
During the Expansion phase, the market begins to recover. Demand for properties increases, leading to rising prices and decreasing vacancy rates. New construction projects start to pick up as developers respond to growing demand. This phase is marked by increased economic growth and consumer confidence.
Key Indicators:
- Rising property prices
- Decreasing vacancy rates
- Increase in new construction
Investment Strategy:
- Hold and Buy: Continue to hold properties for appreciation. Consider buying additional properties as prices are still reasonable.
3. Hyper Supply
The Hyper Supply phase occurs when the market becomes oversaturated with properties. Although prices may still be rising, the rate of increase slows down. Vacancy rates may start to climb as new construction outpaces demand. This phase signals a potential downturn in the market.
Key Indicators:
- Slowing price appreciation
- Increasing vacancy rates
- Excessive new construction
Investment Strategy:
- Sell: Consider selling properties before the market becomes saturated and prices drop.
4. Recession
The Recession phase is characterized by a decline in property values and an increase in vacancy rates. This phase often follows an economic downturn or financial crisis. New construction halts, and the market becomes a buyer’s market.
Key Indicators:
- Declining property prices
- High vacancy rates
- Little to no new construction
Investment Strategy:
- Hold or Buy: Hold properties to ride out the downturn. For those with capital, it can be a good time to buy undervalued assets.
Market Cycle Data: A Snapshot
To illustrate the different phases, here is a table summarizing key data points for each phase:
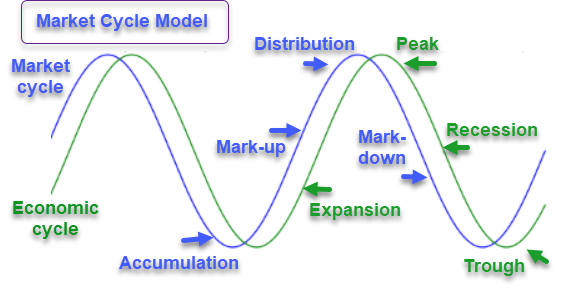
Source: SeekingAlpha
Understanding the real estate market cycle is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By recognizing the signs of each phase, you can better time your buying, holding, and selling strategies to maximize returns. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, staying attuned to these market signals will help you navigate the ever-changing landscape of real estate investing.

